two sample t test survey package|design based t testing : traders This is a tutorial for using the survey package (Lumley 2021) to analyze complex survey data. “Complex” surveys are those with stratification and/or clustering. The package handles weights, and adjusts statistical tests for the survey .
Resultado da Sofhi Boos Centenário, Camaquã - RS, Brasil. 139 km de Pelotas. Entre e escolha as melhores acompanhantes em Pelotas. Sua busca finalmente .
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEBSTORIES Japa Nordestina Vlogs INSTAGRAM 200721 NA ÍNTEGRA A Japa Revela Vários Assuntos PICANTES. CLUBE DA MANSÃO MAROMBA. 8.64K subscribers. .
For comparing two estimates, this is called a two-sample t-test. We can set up the hypothesis test as follows: \(H_0: \mu_1 = \mu_2\) where \(\mu_i\) is the mean outcome for group \(i\) \(H_A: \mu_1 \neq \mu_2\) Two-sample t-tests can also . One-sample or two-sample t-test. This function is a wrapper for svymean in the one-sample case and for svyglm in the two-sample case. Degrees of freedom are degf(design) . I want to perform a two-sample (welch's) t-test on the equality of two means, one of which is obtained using simple random sampling (srsmean), and the other which is calculated .
One-sample or two-sample t-test. This function is a wrapper for svymean in the one-sample case and for svyglm in the two-sample case. Degrees of freedom are degf(design)-1 for the .
One-sample or two-sample t-test. This function is a wrapper for svymean in the one-sample case and for svyglm in the two-sample case. Degrees of freedom are degf(design)-1 for the .This is a tutorial for using the survey package (Lumley 2021) to analyze complex survey data. “Complex” surveys are those with stratification and/or clustering. The package handles weights, and adjusts statistical tests for the survey .Description. Summary statistics, two-sample tests, rank tests, generalised linear models, cumulative link models, Cox models, loglinear models, and general maximum .
One-sample or two-sample t-test. This function is a wrapper for svymean in the one-sample case and for svyglm in the two-sample case. Degrees of freedom are degf(design) for the one . I want to perform a two-sample T-test to test for a difference between two independent samples which each sample abides by the assumptions of the T-test (each . A two sample t-test is used to determine whether or not two population means are equal. This tutorial explains the following: The motivation for performing a two sample t-test. .We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us.
surveyoptions: Options for the survey package; surveysummary: Summary statistics for sample surveys; svrepdesign: Specify survey design with replicate weights; . One-sample or two-sample t-test. This function is a wrapper for svymean in the one-sample case and for svyglm in the two-sample case. Degrees of freedom are degf .
t test with survey design
formula: Formula, outcome~group for two-sample, outcome~0 or outcome~1 for one-sample design: survey design object. for methodsformula: Formula, outcome~group for two-sample, outcome~0 or outcome~1 for one-sample design: survey design object. for methods
refractometer selection guide
Arguments formula. Formula, outcome~group for two-sample, outcome~0 or outcome~1 for one-sample. The group variable must be a factor or character with two levels, or be coded 0/1 or 1/2. design. survey design object. for methodsThere are several kinds of two sample t tests, with the two main categories being paired and unpaired (independent) samples. Paired samples t test. In a paired samples t test, also called dependent samples t test, there are two samples of data, and each observation in one sample is “paired” with an observation in the second sample. The most .Complete the following steps to interpret a 2-sample t-test. Key output includes the estimate for difference, the confidence interval, the p-value, and several graphs. . In these results, the null hypothesis states that the difference in the mean rating between two hospitals is 0. Because the p-value is less than 0.000, which is less than the .
I have a large set of weighted data. I have loaded it into a survey design and would now like to run t-tests on sub-populations. example: DF<-cbind(ID, WEIGHT, GENDER, INCOME) ID WEIGHT GENDER RELOCATE INCOME [1,] 1 4380 1 1 35 [2,] 2 5000 1 1 20 [3,] 3 0 0 1 55 [4,] 4 5640 1 0 60 [5,] 5 6120 0 1 25 example.survey<-svydesign(ids=~0, data=DF, . The motivation for performing a two sample t-test. The formula to perform a two sample t-test. The assumptions that should be met to perform a two sample t-test. An example of how to perform a two sample t-test. Two Sample t-test: Motivation. Suppose we want to know whether or not the mean weight between two different species of turtles is equal.10.1 Introduction. The primary reason for using packages like {survey} and {srvyr} is to account for the sampling design or replicate weights into point and uncertainty estimates (Freedman Ellis and Schneider 2024; Lumley 2010).By incorporating the sampling design or replicate weights, these estimates are appropriately calculated.
design based t testing
$\begingroup$ @BruceET - I mention in the post that I used a Levene test and determined the two groups have different variances. This violates the assumption of homogeneity in variance necessary for a student's t-test, and is why I plan to use the Welch test. Explaining what sample weights are may be out of scope, but it's a very standard procedure in survey . I am currently using R's survey library to analyze survey data. I have two samples from two different time periods. My goal is to test if the difference between the two weighted sample means is equal to 0. Question: How do I approach this using R's survey library? I have tried two approaches to doing this:
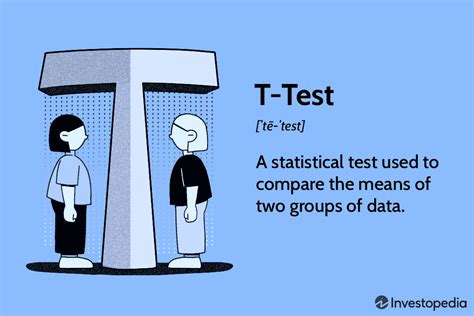
Cohen’s d for two-sample t-test. The grammar in the cohensD function in the lsr package follows that of the t.test function. Note that this function reports the value as a positive number. library(lsr) cohensD(Sodium ~ Instructor, data = Data) [1] 0.2426174. Optional readings “Student's t–test for two samples” in McDonald, J.H. 2014.Student's t-test is a statistical test used to test whether the difference between the response of two groups is statistically significant or not. It is any statistical hypothesis test in which the test statistic follows a Student's t-distribution under the null hypothesis.It is most commonly applied when the test statistic would follow a normal distribution if the value of a scaling term in .
Summary statistics, two-sample tests, rank tests, generalised linear models, cumulative link models, Cox models, loglinear models, and general maximum pseudolikelihood estimation for multistage stratified, cluster-sampled, unequally weighted survey samples. Variances by Taylor series linearisation or replicate weights. Post-stratification, calibration, and raking. Two-phase .
Calculate the T-test for the means of two independent samples of scores. This is a test for the null hypothesis that 2 independent samples have identical average (expected) values. This test assumes that the populations have identical variances by default. . Yuen, Karen K. “The Two-Sample Trimmed t for Unequal Population Variances . Welch's t-Test: Two sample t-Test is used to compare the means of two different independent datasets. But we can apply a Two-Sample T-Test on those data groups that share the same variance. Now to compare two data .
Version info: Code for this page was tested in R version 3.0.1 (2013-05-16) On: 2013-06-25 With: survey 3.29-5; foreign 0.8-54; knitr 1.2 Example 1. This example is taken from Levy and Lemeshow’s Sampling of Populations page 53.. Import the Stata dataset directly into R using the read.dta function from the foreign package: Summary statistics, two-sample tests, rank tests, generalised linear models, cumulative link models, Cox models, loglinear models, and general maximum pseudolikelihood estimation for multistage stratified, cluster-sampled, unequally weighted survey samples. Variances by Taylor series linearisation or replicate weights. Post-stratification, calibration, and .
The t-test will prove or disprove your null hypothesis. Different kinds of t-tests. So far we’ve talked about testing whether there’s a difference between two independent populations, aka a 2-sample t-test. But there are some other common variations of the .
Where: X1 and X2 are the sample means of the two groups.; s1 and s2 are the sample variances of the two groups.; n1 and n2 are the sample sizes of the two groups.; We then need to calculate the p-value using degrees of freedom equal to (n 1 +n 2-1).If the p-value is less than your chosen significance level, we can reject the null hypothesis and say that the . Summary statistics, two-sample tests, rank tests, generalised linear models, cumulative link models, Cox models, loglinear models, and general maximum pseudolikelihood estimation for multistage stratified, cluster-sampled, unequally weighted survey samples. Variances by Taylor series linearisation or replicate weights. Post-stratification, calibration, and .
Learn how to perform one and two sample t-tests on vectors of data using the t.test function in R. Survey research commonly relies on weights to reduce bias and produce a representative sample for a given population of interest. Weighted survey data produces a value assigned to each observation in the data that increases or decreases that observation’s influence (or weight) when performing statistical operations using the data.
Several days ago, I asked a similar question about t-testing, which received an excellent answer, and can be referenced here: R- How to conduct two-sample t-test with two different survey designs. For example, here, I have defined two survey designs: one is simple random sampling, and the other includes weighting and stratification.
Their approach is incorporated in the R survey package “survey” . 2.2 Extension to Quantile Test and Complex Survey Samples. The median test is a special case of a quantile test . . Historical Notes on the Wilcoxon Unpaired Two-Sample Test. Journal of the American Statistical Association. 1957; 52:356–360.We’ll use a two-sample t test to evaluate if the difference between the two group means is statistically significant. The t test output is below. In the output, you can see that the treatment group (Sample 1) has a mean of 109 while the control group’s (Sample 2) average is 100. The p-value for the difference between the groups is 0.112.
refractometer serum protein
refractometer setup
WEB25 de mar. de 2023 · Follow these two simple steps to play pokies for free without making a deposit: Step 1: Pick a bonus from our list and click on Claim Now. Step 2: Register with the casino you have chosen. Make sure you use correct details so that you can verify your account and withdraw your winnings at a later stage.
two sample t test survey package|design based t testing